HTTP / HTTPS Service¶
Introduction¶
This page contains information on the usage and behaviour of the http and https file transfer services.
The HTTP / HTTPS file transfer service provides a HTML-based interface designed to work in any web browser, including older versions of browsers where JavaScript or cookie features are either not supported or enabled.
The same HTTP/HTTPS file transfer service allows receiving files over the AS2 protocol. Check the dedicated AS2 server usage to learn more about the SFTPPlus AS2 server.
There is also a REST JSON API and WebDAV API available, designed to allow 3rd party applications to exchange files with SFTPPlus. Check our developer documentation to learn more about the available APIs.
The HTTP protocol is implemented based on RFC 2616, while the HTTPS protocol is based on RFC 2818.
The Web Manager GUI provides configuration options and status indications to the state of the http or https service:
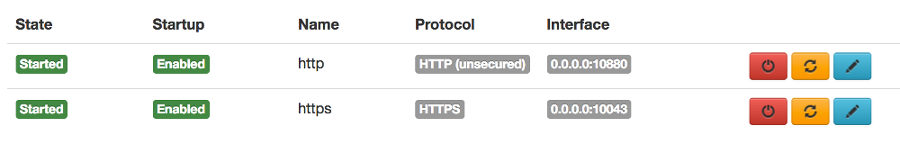
For more details about the configuration options, please go to the dedicated HTTP/HTTPS configuration page.
File management functionality¶
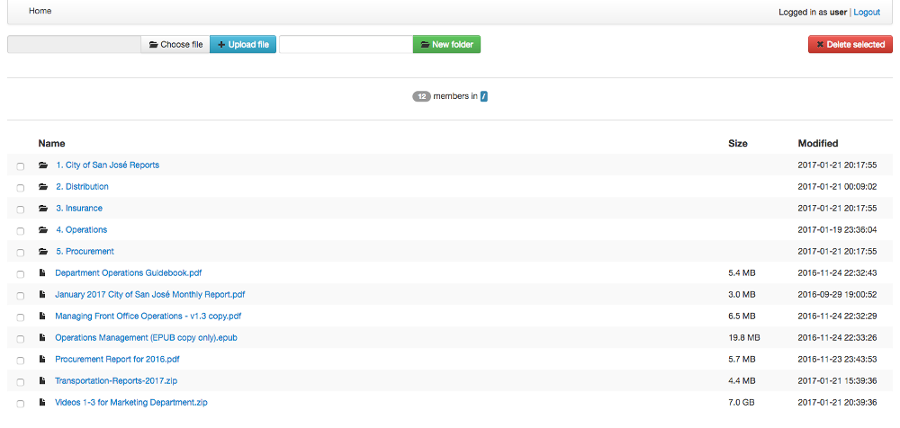
Above is a screenshot of the HTTP / HTTPS file management functionality.
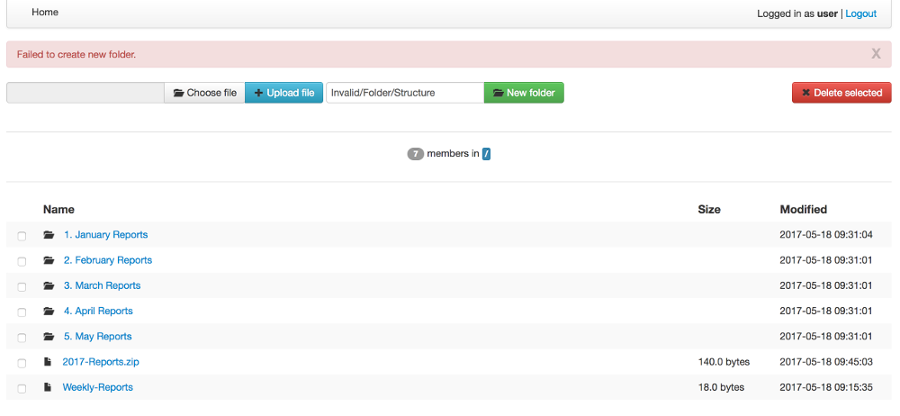
Above is a screenshot of how errors are communicated - in this case, when an invalid folder is being created.
The HTTP and HTTPS service allows the same level of file access as the other available file transfer services such as FTPS or SFTP.
When using the file transfer service in a browser without JavaScript or cookies, some of the advanced features are not available.
Basic features, listed below, are supported:
Authenticate using HTTP Basic Auth method
Navigate folders' structure
Download files
Create new folders
Upload files
Delete files and folders
Recursive deletion of a folder
Legacy UI appearance¶
Latest versions of SFTPPlus include an updated web user interface that for added functionality convenience are using web browser capabilities only available in latest generation web browsers.
For legacy purposes or to avoid disrupting existing web UI file transfer processes, you can configure the HTTP web client to use an older version of the user interface:
[services/9ac4-1054-f0e4]
name = HTTPS File Transfer Service
type = http
ui_version = ui-gen-1
This will use the UI available in SFTPPlus version 4.15.0 or older.
The latest UI version is ui_version = ui-gen-2.
Custom appearance¶
Attention
The custom appearance functionality is released as a feature preview. We encourage you to try this functionality and send feedback. The HTML and CSS markup might be changed in future releases.
The appearance of the HTTP service pages can be customized by overwriting the default CSS of the HTTP service pages and executing custom JavaScript code.
Using the theme_path configuration option you can instruct SFTPPlus to load a custom theme for the HTTP pages.
The theme path should contain at least the following files:
main.css
main.js (only available in gen1)
logo.svg (only available in gen2)
favicon.ico
If you don't need to customize the CSS or JavaScript leave the file empty.
The name of the HTTP/HTTPS service will be used as the page name on the login page and the file browser page.
Note
When changing the service name, you will need to restart the HTTP/HTTPS service. Restarting the whole SFTPPlus application is not required.
The main.css file from the theme path is loaded as the last CSS file. The main.jss file from the theme path is loaded at the end of the page as the last JavaScript file.
The theme files are accessible inside the HTTP service as /__chsps__/theme/.
To load the theme files from C:\File-Server\Theme you need to configure
the service as:
[services/9ac4-1054-f0e4]
name = HTTPS File Transfer Service
type = https
theme_path = C:\File-Server\Theme
For example C:\File-Server\Theme\main.css can make buttons rounder and hide the MFA field on the login page
(while C:\File-Server\Theme\main.js can be empty):
.btn.btn-outlined {
border-radius: 1.125rem;
}
[data-theme="login-mfa-input"] {
display: none;
}
Below is the list of data-theme HTML attributes that control the appearance of parts of the login page:
* `data-theme="login-username-prompt"` Username label and input
* `data-theme="login-password-prompt"` Password label and input
* `data-theme="login-mfa-input"` MFA/TOTP code label and input
* `data-theme="login-no-cookies"` Link to authenticate for browser without cookie enabled
* `data-theme="login-username-password"` Button to authenticate with username/password credentials
* `data-theme="login-oidc"` OpenID Connect or MS Entra ID login label and button
* `data-theme="login-oidc-alternative"` Text presented when OpenID Connect is an alternative login method
* `data-theme="login-footnotes-button"` Button that triggers the login dialog to display terms or service or usage help information.
* `data-theme="login-footnotes-dialog"` UI dialog element in which the terms or service or usage/help information is displayed.
If you find it hard to customize certain UI elements, get in touch with us. We will consider updating the default HTML / CSS markup to make it easier for you to apply custom CSS rules.
Custom service information link¶
You can configure the login page to show a custom link which opens a message box with more info when pressed.
This is done using the login_footnotes configuration option. This configuration option is defined on multiple lines.
To define a link with the text Terms of Service that opens a message box titled ACME Company Terms of Service containing your terms of services, use a configuration similar to this example:
[services/9ac4-1054-f0e4]
name = HTTPS File Transfer Service
type = https
login_footnotes = Terms of Service
ACME Company Terms of Service
Posted: 21 March 2024
Effective: 1 June 2024
Thank you for using our product!
These Terms of Service cover your use of the ACME Company services.
When you use our services, you provide us your files and their content.
These terms don't give us any rights to your content, except for the limited rights that enable us to offer these services.
Load balancer¶
The HTTP/HTTPS services of SFTPPlus can be integrated in a load balancing solution.
SFTPPlus requires no extra configuration when functioning behind a layer 4 TCP balancer or DNS load balancer.
AWS Network Load Balancer and Azure Load Balancer are examples of layer 4 load balancers.
For Layer 4 load balancers, make sure the forwarded traffic has a persistent session based on the client's source IP address.
When using a layer 7 HTTP/HTTPS load balancer, you will need to adjust Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) protection. This is because the HTTP load balancer is not updating some of the headers found in the initial request when forwarding a request to the load balanced node. This result in a request that appears to be coming from a different site.
AWS Application Load Balancer and Azure Application Gateway are examples of Layer 7 load balancers.
For HTTP / Layer 7 load balancers, make sure the forwarded traffic has sticky sessions enabled.
When the HTTP/HTTP file transfer service is not configured for the load balancer, you will see 400 Possible CSRF errors.
When the load balancer is configured with the listeners
https://files.example.com on default port 443 and
https://www.example.com on port 10443, and it
forwards all requests to SFTPPlus at http://worker1.example.com,
you will need to configure SFTPPlus as follows:
[services/9ac4-1054-f0e4]
name = HTTPS File Transfer Service
type = http
address = worker1.example.com
port = 18080
accepted_origins = files.example.com, www.example.com:10443
If you have an HTTP (unsecure) load balancer that is accesses by the users as
http://files.example.com and it forwards all requests to SFTPPlus at http://worker1.example.com,
you will need to configure SFTPPlus as follows,
adding http as the first value for accepted_origins:
[services/9ac4-1054-f0e4]
name = HTTPS File Transfer Service
type = http
address = worker1.example.com
port = 18080
accepted_origins = http, files.example.com
Public site¶
SFTPPlus can serve as a public file transfer server. Visitors can access files on the server without prior authentication. This is similar to the Anonymous mode available in the FTP server, with the exception that no username is required.
To enable public access, you need to explicitly define an application account to be used for handling the files via the public interface.
The account will define the path from where the public files are served and the permissions used for each file.
The public site is not limited to read-only access. Visitors of the public site will have the same access as defined in the public account configuration.
The public file access is recorded in the audit log under the configured account. It is recommended to set up a dedicated account for the public access and not to reuse an existing account.
Below is an example for a general download-only public root access,
which will deny downloading any .exe. file and
allow uploading files inside the /reports/ folder.
The public files will be available at the following URL: https://example.tld/public-access.
In this example, public access will no longer be available after the 23rd of March 2025, when the public account is set to expire.:
[services/9ac4-1054-f0e4]
name = HTTPS File Transfer Service
type = https
public_account_uuid = 92ad5b32-d8d7-4ed8-94e1-dbb9f01383f4
public_name = public-access
[accounts/92ad5b32-d8d7-4ed8-94e1-dbb9f01383f4]
name = public-http
type = application
description = Files available without password over HTTP.
group = 95373161-b944-4d70-af5e-cab1976cc535
home_folder_path = /local/path/to/public/files
permissions =
allow-read, allow-list
*.exe, deny-full-control
/reports/, allow-write
expire_datetime: 2025-03-23
[groups/95373161-b944-4d70-af5e-cab1976cc535]
name = http-group
virtual_folders: /shared, /ftp-files/shared
The create_home_folder and home_folder_structure account and group configurations are ignored for the public HTTP access.
Authentication process¶
The HTTP file transfer service will use a single cookie to manage the authentication process.
A single session cookie is used for all the file transfer operations.
The session cookie is set with httpOnly and sameSite options. For the HTTPS service, cookies are set with the secure option.
For simple usage via the command line with tools like as cURL or Wget, HTTP Basic Auth is available.
Warning
HTTP Basic Auth will send credentials in a plain text encoding and it is not recommended to use HTTP Basic Auth over unsecured HTTP connections.
HTTP/1.1 100 Continue status code¶
HTTP/HTTPS file transfer service can handle HTTP/1.1 client requests made using the 100 (Continue) status. This allows the client sending the request message with a given request body to determine whether the origin server is willing to accept the request (based on the request headers) before the client sends the request body.
For example, it might be inappropriate or highly inefficient for the client to send a large body if the server rejects it solely based on the body size.